What is PCOD?
Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) is a medical condition in which a woman’s ovaries generate immature or partially mature eggs in large numbers during reproductive age. These eggs develop into cysts in the ovaries over time. Due to the cysts, ovaries become large & secrete large amounts of male hormones (androgen) which causes infertility problems, irregular periods, unwanted weight gain, and other health issues.
While relatively common, most women are not aware of the signs and symptoms of PCOD, the implications of the condition, and available treatment options. So let us take a closer look.
What Problem PCOD May Cause?
The symptoms associated with PCOD often leave a lasting impact on women’s physical and mental well-being. It is estimated that about 34% of the women suffering from PCOD problems also suffer from depression, and nearly 45% suffer from anxiety. This makes it essential to diagnose and manage the symptoms early to prevent PCOD problems in the future.
Many of the women diagnosed with PCOD problems also experience poor quality of life-related to:
- Mood swings
- Negative social relationships
- Low self-confidence
- Negative self-image
- Disruption of eating and sleep patterns
- Low motivation
Difference Between PCOD and PCOS
The names PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome) and PCOD full form Polycystic Ovarian Disease are often used interchangeably. Let us look at how we can differentiate between PCOD vs PCOS.
PCOD
PCOD is a medical condition where the women’s ovaries produce immature or partially impure eggs, which transform into cysts.
About one-third of women worldwide suffer from PCOD, which is pretty common.
PCOD does not affect fertility in women. In about 80% of the cases, women can conceive with little help and medications.
PCOD has no serious complications.
PCOD doesn’t have severe complications and can be healed with the right diet plan.
PCOD does not release as many male hormones as PCOS, the symptoms are less frequent and rarely noticeable.
Women who suffer from PCOD experience mild to moderate symptoms. These symptoms can be managed with diet, lifestyle changes, and medication.
If you experience any of the symptoms associated with PCOD, it is important to consult an expert gynecologist for a proper diagnosis and PCOD problem treatment.
PCOS
PCOS is a more severe condition where the ovaries produce a high quantity of male hormones, resulting in excess cyst formation.
PCOS is a disease that affects fewer women than PCOD.
PCOS affects female fertility adversely. As the woman is not ovulating regularly, it is difficult to conceive. Even if they do, there is a risk of miscarriage, premature birth, or complications during pregnancy.
Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, heart disease, and advanced endometrial cancer are serious complications associated with PCOS.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) cannot be cured, the symptoms can be controlled through lifestyle changes and medicines.
Women suffering from PCOS often struggle with the symptoms from a younger age.
PCOS is inherently a metabolic disorder. This means it is often accompanied by a greater risk of developing high blood pressure (hypertension), diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, obesity, and cancers of the uterus and breast.
Women suffering from PCOS may require infertility treatments and active treatment protocols to manage other health conditions that they may develop.
Your gynecologist may refer you to an endocrinologist or a cardiologist to help manage other health conditions that you develop due to PCOS.
PCOD/PCOS Problem Symptoms
PCOD primarily affects the ovaries. The ovaries are a part of the female reproductive system. All women have two ovaries, and these release egg cells or ova. The ovaries are responsible for the production of estrogen and progesterone. They also release the male hormone called androgen. PCOD can disrupt this process and lead to an abnormal release of male hormones.
Here are some common signs and symptoms of PCOD/PCOS problems:
- Irregular or unpredictable menstrual periods
- Heavy bleeding during periods
- Excess body hair
- Acne
- Hair loss or male pattern baldness
- Difficulty in getting pregnant
- Obesity
- Darkening of skin or pigmentation around the neck
- Sleep disorders
- Depression
PCOD/PCOS Causes
The exact cause of the PCOD problem remains unclear. Doctors believe that PCOD can have both genetic and environmental causes. PCOD is often associated with:
- An unhealthy diet
- A sedentary lifestyle
- Pollution
- Hormone altering medication
- Several OTC (over-the-counter) medications and supplements
In many cases, PCOD problem runs in families and is also considered hereditary. Researchers point to several physiological causes that may increase your risks of developing PCOD/PCOS:
Excess Insulin Production:- Insulin is a natural hormone produced by the pancreas. It helps regulate the metabolic functions of the body and regulate blood sugar levels. Doctors believe that a high insulin level is one of the key drivers of PCOS. Excess insulin also prompts the body to increase the production of androgen (male hormone), which inhibits ovulation.
Inflammation:– Several physiological reasons may cause low-grade inflammation in the body. Mild forms of autoimmune diseases can also cause inflammation in the body’s tissues. This, in turn, again increases the androgen levels in the body.
High Androgen Levels:– The male hormone is associated with increased facial and body hair, acne outbreaks and skin issues, and a higher risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
PCOD Problem Treatment Options
It is important to remember that solutions to the Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) problem involve both medication and lifestyle changes. Unfortunately, there is no known cure for the condition, but managing the symptoms can improve the quality of life.
Diet modification can go a long way in managing symptoms and offering PCOD problem solutions. Even a 5% reduction in body weight can help reduce the symptoms significantly. Eliminating sugars and fatty foods can help lower the risk of developing diabetes, high cholesterol levels, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Even a 5% reduction in body weight can help reduce the symptoms significantly.
- Eliminating sugars and fatty foods can help lower the risk of developing diabetes, high cholesterol levels, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Women leading a sedentary lifestyle must plan and stick to a regular exercise schedule as part of the PCOD solution.
- Cyclic hormonal treatment and ovulation induction medication can help regulate the menstrual cycle.
- Skin treatment can help reduce acne and the darkening of the skin.
- Infertility treatment can help with conception.
- Laparoscopic surgery can help destroy androgen-producing tissue.
- Regular monitoring of health and hormone levels can help prevent PCOD problems in the future.
The symptoms associated with Polycystic Ovarian Disease (PCOD) can be treated with the help of several medicines. In rare cases, your doctor may recommend surgery as well. Some of the treatment protocols for PCOD/PCOS include:
Progestin – Progestin, a synthetic progestogen, is often recommended to correct amenorrhea or the absence of periods.
Birth control pills – Some birth control pills contain estrogen and progestin and help reduce the Androgen levels in the body. This helps combat anovulation.
Letrozole and clomiphene – Letrozole and clomiphene help induce ovulation.
Metformin – Metformin reduces insulin resistance and helps with weight reduction as well.
Immature follicle aspiration – Helps reduce the number of immature follicles, improving ovulation.
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling – Laparoscopic drilling is a minimally invasive surgery that helps lower testosterone levels produced by the ovaries.
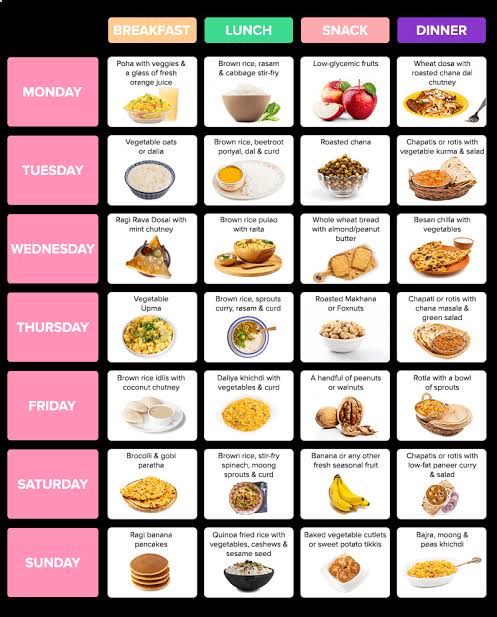
PCOD/PCOS Diet
Diet is an essential component of PCOD problem treatment and symptom management. Weight loss through dietary modifications can help:
- Reduce blood glucose and HbA1C levels, lowering your diabetes risk
- Lower insulin
- Improve cholesterol levels
- A low carbohydrate diet is extremely helpful in losing weight and reducing BMR.
- Fresh foods like vegetables and fruits are low in glycaemic index (GI) and help with weight reduction and diabetes management.
- Avoid processed and packaged foods to lower the risk of hypertension.
Maintaining good health is essential for preventing and treating hormonal disorders and conditions. The best treatment for PCOD and PCOS includes early diagnosis and following a good diet plan.
PCOD and Mental Health
PCOD is associated with a high prevalence of anxiety and depression. PCOD/PCOS is a condition that requires active, long-term management. The role of a support system in the maintenance of treatment protocols over the long term is a major one.
Women with PCOD/PCOS often suffer from low self-image and body-image issues due to excess body hair, weight gain around the abdomen area, skin darkening and pigmentation around the neck, etc. While these symptoms can be treated, friends and family must remain supportive for the woman to maintain positive mental health.
The hormonal imbalance in this condition makes the woman more prone to stress and anxiety. In addition, infertility issues and miscarriages occurring in PCOS can cause depression. Seeking therapy and help can be important in such situations.
Like to Read: Powerful Self-Care Tips to Boost Your Mental Well-Being
What Hormones Affect PCOS?
People with PCOS have a hormonal imbalance that disrupts their menstrual cycle, ovulation, and possibly, conception. These hormones are like an intricate web and the function of your reproductive system relies heavily on its balance. The hormones that play a role in PCOS are:
- Androgens (like testosterone and androstenedione)
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
- Insulin
Conclusion
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a complex hormonal disorder that affects millions of individuals, primarily those of reproductive age. It is characterized by irregular menstrual cycles, excessive androgen levels, and the presence of multiple cysts in the ovaries. PCOS is linked to a range of metabolic and reproductive issues, including infertility, insulin resistance, obesity, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
The exact cause of PCOS remains unclear, but genetic and environmental factors play a significant role. Lifestyle modifications, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, are often recommended as first-line treatments to manage symptoms. Medications, including hormonal contraceptives and insulin-sensitizing drugs, may also be prescribed.
PCOS not only affects physical health but also has psychological implications, increasing the risk of anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. Early diagnosis and proper management are crucial in reducing long-term complications. More awareness, research, and support systems are needed to help those affected by PCOS lead healthier lives. While there is no cure, effective symptom management can significantly improve the quality of life.


Heya i’m for the first time here. I came across this board and I find It really helpful & it helped me out a lot. I’m hoping to provide something back and aid others such as you aided me.
sure.