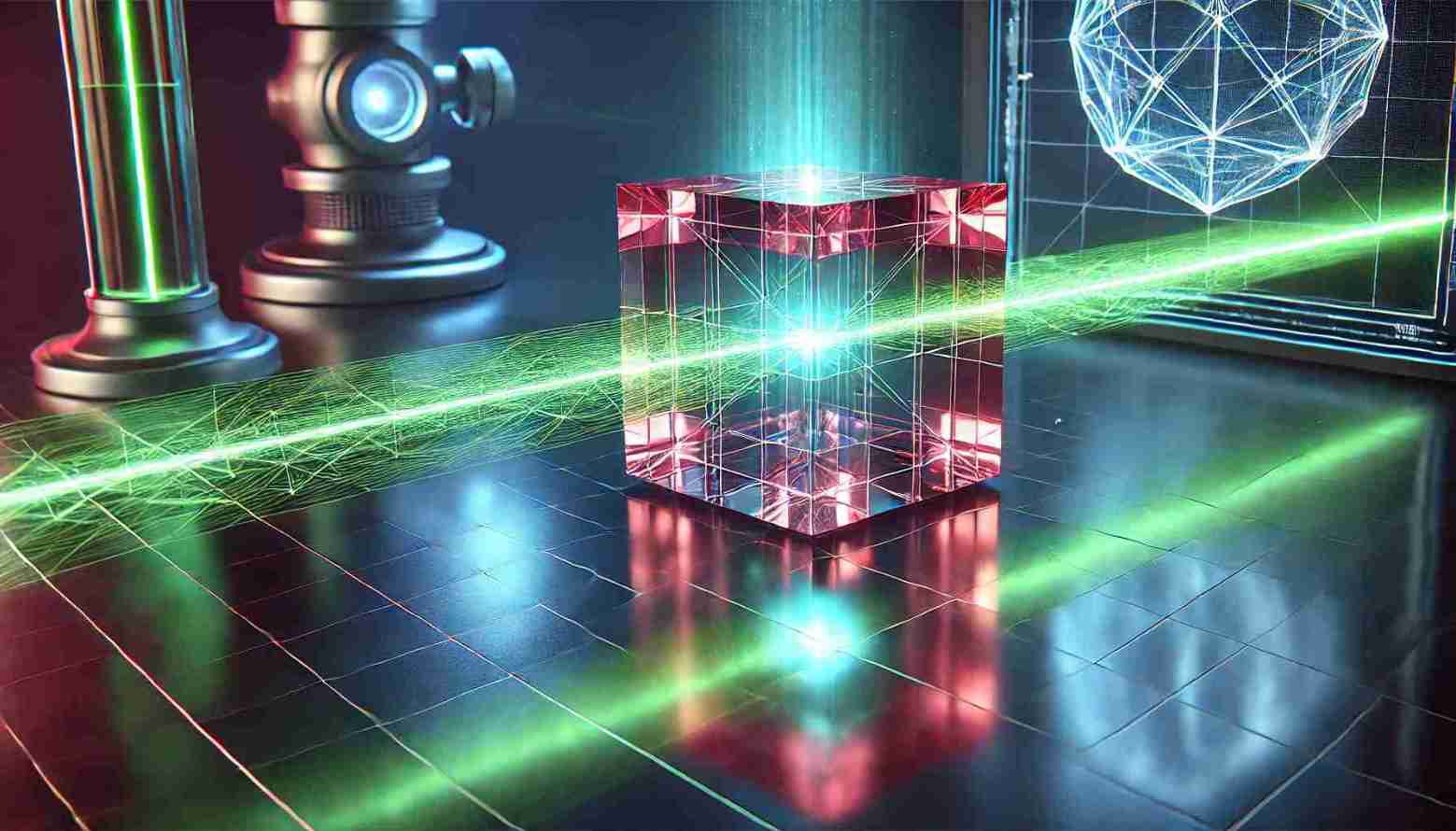
Break Through Discovery
Experimental Set-Up
With the help of a ruby cube and two laser beams, researchers made one ray of light cast a shadow when illuminated by the other.
Light normally makes other objects cast shadows – but with a little help from a ruby, a beam of laser light can cast a shadow of its own.
When two laser beams interact, they don’t clash together like lightsabers in Star Wars, says Raphael Abrahao at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York. In real life, the National Laboratory in New York. In real life, they will simply pass through each other. Abrahao and his colleagues, however, found a way for one laser beam to block another and make its shadow appear.
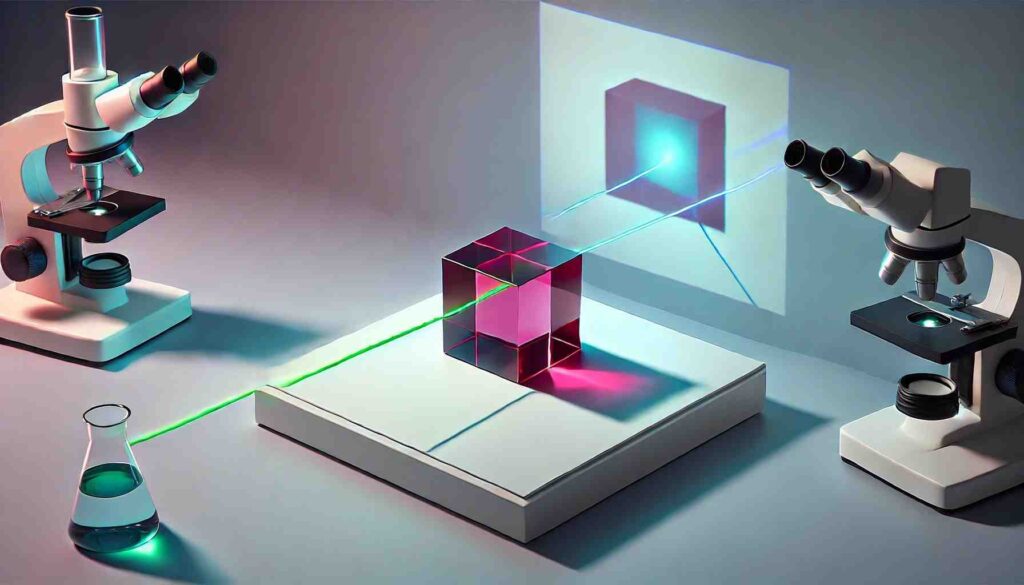
The crucial ingredient was a ruby cube. The researchers hit this cube with a beam of green laser light while illuminating it with a blue laser from the side. As the green light passed through the ruby atoms, it changed their properties in a peculiar way that then affected how they reacted to the blue light.
Instead of letting the blue laser pass through them, the atoms affected by the green light now blocked the blue light, which created a shadow shaped exactly like the green laser beam. Remarkably, the researchers could project the blue light on a screen and see this “shadow of a laser” with the naked eye.
Self-Shadowing Effect
The research, published in the prestigious journal Nature Physics, outlines the meticulous experiments carried out by an international team of physicists led by Dr. Evelyn Reed from Cavendish Laboratory in Cambridge. He described the phenomenon as “entirely unexpected and initially quite perplexing.” According to him, he is a newcomer to quantum optics but only recently came upon it while working with colleagues on a project concerning light interactions with some newly discovered negative refractive index materials.
These materials have generated much interest in their abnormal optical behavior for application toward making “superlenses,” which could approach resolution scales hundreds of orders better than conventional optics. To get to this measurement, the researchers used a bit of a kludge experimental set-up with an otherwise very fine-tuned laser system to emit extremely short-pulse, ultrahigh-peaked power levels of light that are paired here with a construction of metamaterial. It was nanoscale in structure, its structures intricately arrayed for the control of the electromagnetic field in ways previously unattained.
As these researchers watched as light propagated through the metamaterial, they also saw a bright shadow cast by light itself a phenomenon running directly contrary to the very most basic understanding that had been the basis of this propagation of light as explained within the classical model. “Initially, we thought it was a flaw in our experimental setup,” said Dr. Reed in a news conference held in the Cavendish Laboratory. “We spent months meticulously checking and rechecking our equipment, our calculations, everything.
But the shadow persisted, consistently and reproducibly.” The persistence of the test eliminated any kind of experimental fault, thus further confirming the existence of their very astonishing discovery. How can one explain that the light itself casts a shadow? Sounds paradoxical, the light may cast a shadow.
Actually, this occurs when the light pulse interacts with metamaterial structures at the nanoscale and, in fact, causes a transitory change in the refractive index of the material based on the interaction between the pulse of light and the material. This, in turn, leads to an area of localized decrease of optical density that plays a role of the temporary barrier for the advancement of the pulse of light further.
This occurs due to the localized reduction of density caused by further scattering of light. According to the researchers, this is where the self-shadowing effect originates from the interaction of light and matter at a nanoscale level, but with non-linear interactions. These cannot be simply explained by using the classical model of optics founded on linear approximations. As such, self-shadowing reflects the inability of the classical model to explain complex light behavior within complex environments.
Abrahao says he and his colleagues had a long discussion of whether what they created really qualified as a shadow. Because it moved when they moved the green laser beam, they could see it without any special equipment and they managed to project it onto commonplace objects, like a marker, they ultimately decided in the affirmative.
Historically, understanding shadows has been crucial for understanding what light can do and how we can use it, he says, and this experiment adds an unexpected technique into scientists’ light-manipulation toolbox.
Tomás Chlouba at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg in Germany says the experiment uses known processes to create a striking visual demonstration of how materials can help control light. The ruby’s interactions with the laser, for instance, are similar to those of materials used in laser eye surgeries, which must be able to respond to laser light by blocking it if it gets dangerously intense
Implications
The discovery implies profound consequences for our perception of light and of its relationship to matter. It threatens an entire class of presumptions by the classical optics approach by opening up fully novel avenues into investigating the very nature of light. The possible fields of applications certainly go far beyond pure physics concepts the mere practicality of having such ability makes it even quite revolutionary, perhaps.
On more interesting points, it applies all at microscopic scales. The sensitivity to manipulate at such a minute scale may hold the possibility for creating super-resolution microscopes to theoretically image biologic structures at unprecedented high detail levels through which new comprehension in cellular processing and mechanisms in disease can be gained.
This can be employed to revolutionize medical diagnostics and treatment by being able to spot diseases earlier and more accurately and employ better therapies. Of course, it can change telecommunications, too. It is through this that would allow one better control for lighting propagation than to date so as to form relatively more compact, efficient optical devices as a means, among others for transferring data very swiftly. A way of accelerating the web at rapid speeds.
Increasing range of cellular coverage. Adding complexity for phone devices Advanced techniques for forming optical computer applications. Given the ability of light to generate its own shadow, new families of optical logic gates can be envisioned, which would form the building blocks of strong, power-efficient computers.
Such computer systems can potentially enhance computing performance manyfold, achieving even higher velocities of computation and dealing with orders of magnitude more complex arithmetic operations. Therefore, this work on self-shadowing light makes an enormous stride forward in furthering man’s grasp of the most elementary laws of physics.
Future Challenges
It challenged old-fashioned assumptions and ushered in novel, exciting possibilities for scientific and technological progress. Indeed, yet to be discovered fully, there is no question that this science has transformative innovative potential. Dr. Reed and her research team are already committed to further studies that will enable the full understanding and exploitation of this revolutionary phenomenon, opening the doors to a new era of optical technologies that may very soon change our world in thousands and thousands of ways.
The future of optics seems brighter than ever: literally and figuratively. Light’s secrets remain unraveled, and with this discovery, it seems as though the sky has no end. The journey is just at the beginning, and the scientific world is anxiously waiting for the next page of this story to unfold. Huge implications abound in fields ranging from medicine to computing at present, and there is still much to be uncovered, so it is a historic moment for physics and technology.

