The neuroscience of happiness
Happiness is a complex emotional state influenced by various psychological, social, and biological factors. In recent years, neuroscience has shed light on the mechanisms behind happiness, revealing how our brains process and regulate this vital aspect of human life. Understanding the neuroscience of happiness can empower us to cultivate well-being and improve our mental health.
Brain’s Reward System
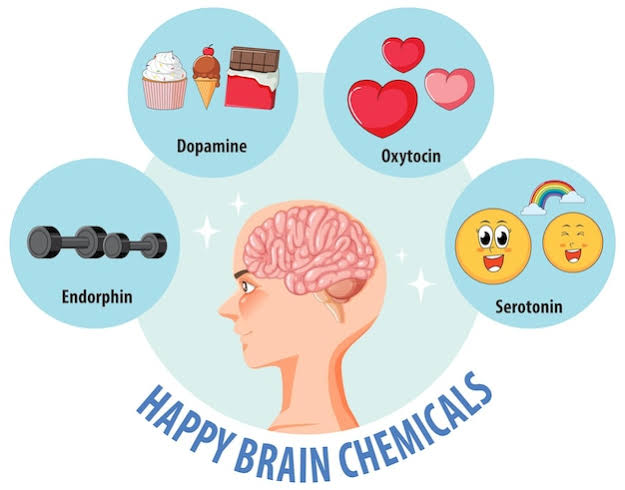
The brain’s reward system is at the heart of happiness, primarily involving neurotransmitters like dopamine, serotonin, and endorphins. The reward system is activated when we engage in activities that promote survival, such as eating, socializing, or achieving goals. This activation releases dopamine, often referred to as the “feel-good” neurotransmitter. When dopamine is released, we experience pleasure and satisfaction, reinforcing behaviors that lead to happiness.
Research shows that activities like exercise, social interactions, and even small achievements can stimulate dopamine release. This not only enhances mood but also motivates us to pursue further rewarding experiences. Understanding this mechanism can help individuals identify activities that promote their happiness.
Role of Serotonin
Serotonin is another crucial neurotransmitter linked to mood regulation. It is often called the “happiness hormone” due to its significant role in influencing emotional well-being. Low levels of serotonin have been associated with depression and anxiety, while higher levels contribute to feelings of happiness and calmness.
Activities that boost serotonin levels include regular physical exercise, exposure to sunlight, and certain dietary choices, such as consuming foods rich in tryptophan (like turkey and nuts). Practicing mindfulness and engaging in social connections can also enhance serotonin production, highlighting the importance of lifestyle choices in maintaining emotional health.
Mindfulness and Happiness
Mindfulness, the practice of being fully present and engaged at the moment, has gained significant attention for its positive effects on mental health. Neuroscientific research indicates that mindfulness meditation can lead to structural and functional changes in the brain, particularly in areas related to emotional regulation and self-awareness.
For example, mindfulness can increase the thickness of the prefrontal cortex, which is involved in complex cognitive behavior and decision-making, and decrease activity in the amygdala, the brain region associated with stress responses. These changes contribute to reduced anxiety and improved emotional resilience, fostering a greater sense of happiness.
Connection Between Exercise and Happiness
Physical activity is a powerful promoter of happiness, primarily due to its ability to enhance neurotransmitter levels. Exercise increases the production of endorphins, which are natural mood lifters. Additionally, it boosts dopamine and serotonin, creating a robust biochemical environment conducive to happiness.
Research suggests that even moderate exercise, such as walking or cycling, can lead to significant improvements in mood and well-being. The social aspect of group activities can also enhance feelings of connection and happiness, illustrating the multifaceted benefits of physical activity.
Social Connections and Neurobiology
Human beings are inherently social creatures, and our relationships profoundly impact our happiness. Neurobiological studies indicate that social interactions activate brain regions associated with reward and positive emotions. The release of oxytocin, often called the “bonding hormone” during social interactions further reinforces feelings of connection and happiness.
Strong social networks provide emotional support, enhance resilience during difficult times, and contribute to a greater sense of belonging. Cultivating and maintaining meaningful relationships is essential for long-term happiness.
Positive Thinking and Its Neural Impact
The power of positive thinking extends beyond mere optimism; it has a tangible impact on brain function. Positive thoughts can lead to the release of dopamine and other neurotransmitters associated with happiness. Neuroscience shows that positive thinking can create new neural pathways, reinforcing a positive mindset over time. Practicing techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) can help individuals reframe negative thoughts and cultivate a more positive outlook, leading to lasting improvements in mental health and happiness.
Sleep and Emotional Regulation
Sleep plays a crucial role in emotional regulation and overall well-being. Research shows that sleep deprivation negatively affects mood and increases susceptibility to anxiety and depression. During sleep, the brain processes emotions and consolidates memories, which is essential for maintaining a balanced emotional state.
Prioritizing good sleep hygiene such as establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a restful environment, and minimizing screen time before bed can significantly enhance mood and contribute to feelings of happiness.
You may also want to read: Digital Detox: Reclaiming Your Time and Mind
